Staging Upsert Output
Overview
Section titled “Overview”The Staging Upsert Output step first looks up a row in a table using one or more lookup keys. If the row can’t be found, it inserts the row. If it can be found and the fields to update are the same, nothing is done. If they are not all the same, the row in the table is updated if the “Variation number” is larger the the existing one.
Configuration Options
Section titled “Configuration Options”| Option | Description |
|---|---|
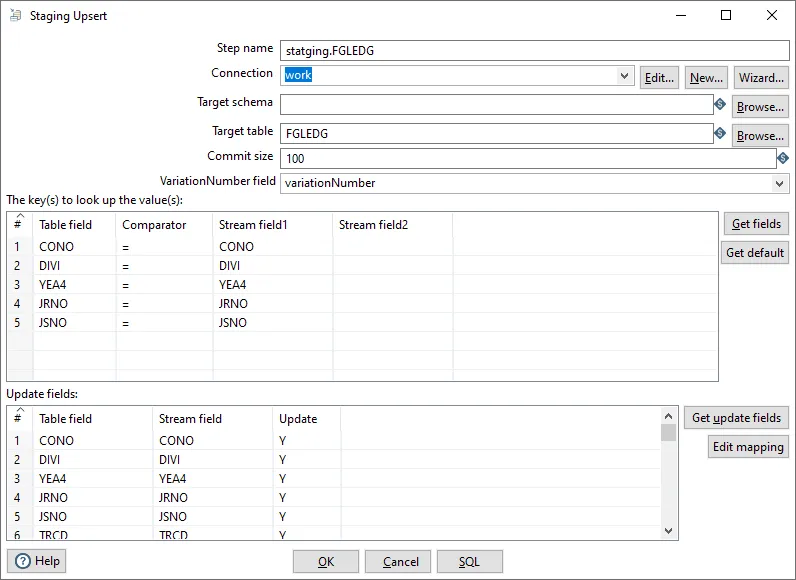
| Step name | Name of the step |
| Connection | Select predefined database connection |
| Target schema | The name of the Schema for the table to write data to. This is important for data sources that allow for table names with dots ’.’ in it |
| Target table | Name of the target table |
Lookup Keys
Section titled “Lookup Keys”The transform uses one or more fields from the input stream as lookup keys to find existing rows in the target table. These keys should match the primary key or unique index columns in the target table for optimal performance.
Variation Number
Section titled “Variation Number”The variation number is a field in both the input stream and the target table that determines whether an update should occur. The update logic works as follows:
- If the row is not found → Insert the new row
- If the row is found and all fields are identical → No action (skip)
- If the row is found and fields differ:
- If input variation number > existing variation number → Update the row
- If input variation number ≤ existing variation number → No action (skip)
This mechanism allows you to control which version of data should be kept when multiple updates occur, useful for handling data from different sources or processing runs.
Best Practices
Section titled “Best Practices”Performance Optimization
Section titled “Performance Optimization”- Index lookup keys: Create indexes on the lookup key columns in the target table
- Batch processing: Process data in batches when possible to reduce database load
- Commit size: Use appropriate commit sizes to balance performance and transaction safety
Data Quality
Section titled “Data Quality”- Validate lookup keys: Ensure lookup key values are not null before processing
- Handle duplicates: Ensure input data has unique lookup key combinations
- Variation number logic: Design your variation number logic carefully to ensure correct update behavior
Common Patterns
Section titled “Common Patterns”This transform is commonly used in combination with:
- Get Timestamp: To get the last processed timestamp for incremental loads
- Filter Rows: To filter data before upserting
- Deem Java Expression: To calculate variation numbers or transform data before upserting
Related
Section titled “Related”- Transforms Overview - Overview of all transforms
- Indexed Table Output - Alternative table output method
- Bulk Loader - Bulk load to databases
- Get Timestamp - Get timestamp for staging pipelines